 Virtlet
Virtlet
what is Virtlet
Virtlet is a Kubernetes CRI (Container Runtime Interface) implementation for running VM-based pods on Kubernetes clusters. (CRI is what enables Kubernetes to run non-Docker flavors of containers, such as Rkt.) For the sake of simplicity of deployment, Virtlet itself runs as a DaemonSet, essentially acting as a hypervisor and making the CRI proxy (Provides the possibility of mixing docker-shim and VM based workloads on the same k8s node) available to run the actual VMs This way, it’s possible to have both Docker and non-Docker pods run on the same node.
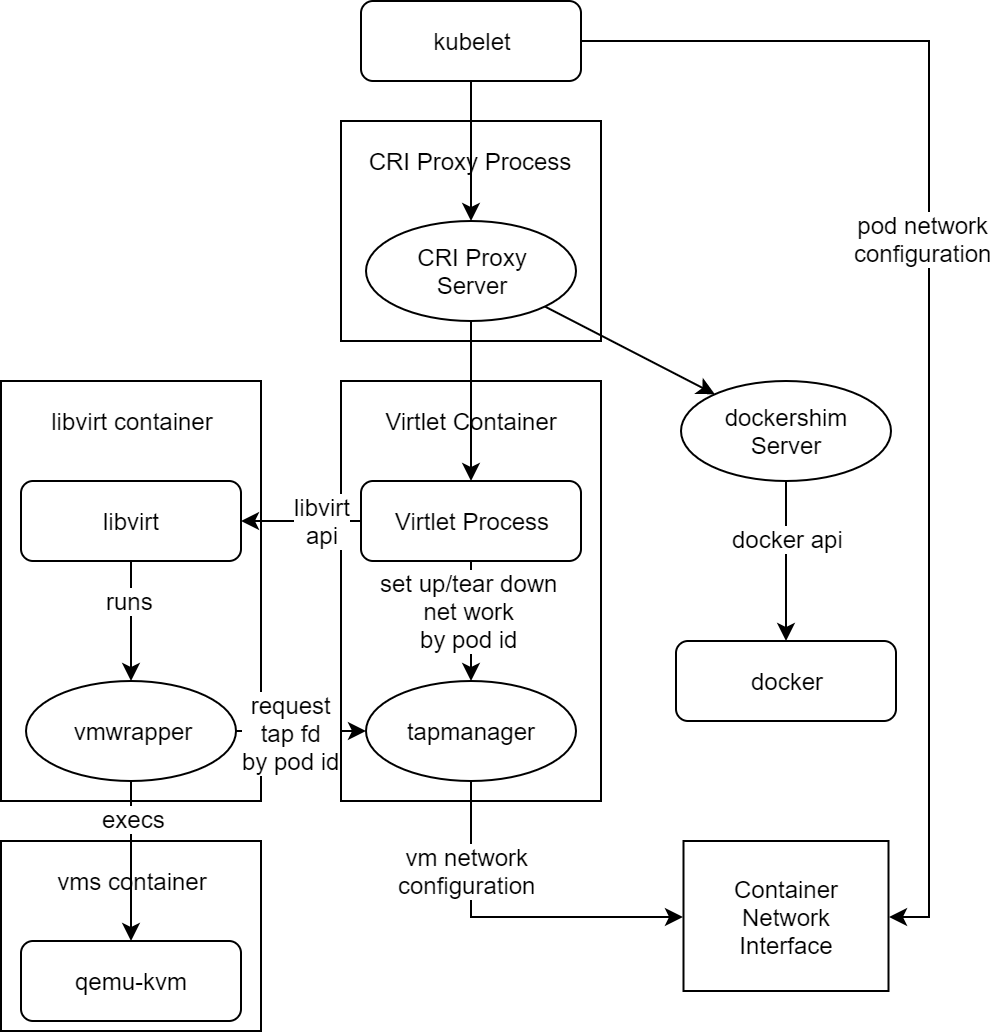
Components
- Virtlet manager: Implements the CRI interface for virtualization and image handling
- Libvirt: The standard instance of libvirt for KVM.
- vmwrapper: Responsible for preparing the environment for the emulator
- Emulator: Currently qemu with KVM support (with possibility of disabling KVM for nested virtualization tests)
- ...
VM Pod Lifecycle
Startup
Delete
- kubelet notices the pod being deleted.
- kubelet invokes StopContainer CRI calls which is getting forwared to Virtlet based on the containing pod sandbox annotations.
- Virtlet stops the libvirt domain. libvirt sends a signal to qemu, which initiates the shutdown. If it doesn't quit in a reasonable time determined by pod's termination grace period, Virtlet will forcibly terminate the domain, thus killing the qemu process.
- After all the containers in the pod (the single container in case of Virtlet VM pod) are stopped, kubelet invokes StopPodSandbox CRI call.
- Virtlet asks its tapmanager to remove pod from the network by means of CNI DEL command.
- after StopPodSandbox returns, the pod sandbox will be eventually GC'd by kubelet by means of RemovePodSandbox CRI call.
- Upon RemovePodSandbox, Virtlet removes the pod metadata from its internal database.
Virtlet is used to create a virtual machine to support some necessary features needed by ICN. In ICN use case we need IpSec to finish some functions. So using QAT devices to speed up the connections is important. But after tests, I found that virtlet doesn't recognize the qat vf device.
Gaps
- Virtlet considers all other devices bound vfio-pci drivers as a volume device and add them into libvritxml as block disk type with disk driver. This will caused vm startup errors.
- Virtlet binds the network devices after the creatition of libvirt domain file, and its default hostdev id number starts from 0, it will make conflict when we add other type device to libvirt domain file by pci-passthrough
- Virtlet can not recognize other sriov device
- ...
To solve these problems, we should first have a clear knowledge of device plugin. A related concept for device plugin is kubernetes extended-resources. In conclusion, By sending a patch node request to the kubernetes apiserver, a custom resource type is added to the node, which is used for the quota statistics of the resource and the corresponding QoS configuration.
Example
To send a patch node request conveniently, we first execute kube proxy command to start it temporarily, then add six intel.com/devices resource to a node (~1 in the commands will automatically transform into /):
curl --header "Content-Type: application/json-patch+json" \
--request PATCH \
--data '[{"op": "add", "path": "/status/capacity/intel.com~1devices", "value": "6"}]' \
http:
|
|---|
Now we extend 6 intel.com/devices resources for your node, then we can see
kubectl describe node xxx
...
Capacity:
ephemeral-storage: 3650656984Ki
cpu: 72
memory: 263895388Ki
intel.com/devices: 6
pods: 110
...
|
|---|
Now we can use these resources in our pod by adding intel.com/devices: "1" to spec.containers.resources.requests/limits and the pod will be scheduled with statistics.
To clean up the extended resources, execute the following commands:
curl --header "Content-Type: application/json-patch+json" \
--request PATCH \
--data '[{"op": "remove", "path": "/status/capacity/intel.com~1devices"}]' \
http:
|
|---|
Device plugin
Overview
Kubernetes provides to vendors a mechanism called device plugins to finish the following three tasks, device plugins are simple gRPC servers that may run in a container deployed through the pod mechanism or in bare metal mode.
service DevicePlugin {
// returns a stream of []Device
rpc ListAndWatch(Empty) returns (stream ListAndWatchResponse) {}
rpc Allocate(AllocateRequest) returns (AllocateResponse) {}
} |
|---|
- advertise devices.
- monitor devices (currently perform health checks).
- hook into the runtime to execute device specific instructions (e.g: Clean GPU memory) and to take in order to make the device available in the container.

Why device plugin
- Very few devices are handled natively by Kubelet (cpu and memory)
- Need a sustainable solution for vendors to be able to advertise their resources to Kubelet and monitor them without writing custom Kubernetes code
- A consistent and portable solution to consume hardware devices across k8s clusters to use a particular device type (GPU, QAT, FPGA, etc.) in pods
- ...
How it works
In kubernetes, kubelet will offer a register gRPC server which allows device plugin register itself to kubelet. When registing itself to kubelet, it will notify kubelet of the following information:
- Its own unix socket name, which will receive the requests from kubelet through the gRPC apis.
- The api version of device plugin itself
- The resource name offered by the device pluigin. The resource name must follow a specified format. such as intel.com/qat
After successful registration, kubelet will call the ListAndWatch function from device plugin. A ListAndWatch function is for the kubelet to Discover the devices and their properties as well as notify of any status change (device became unhealthy)
Enable QAT supported by virtlet
Bug detection in source code
Fix
Example

