...
We do not intend to make any changes to the existing kubernetes API in order to implement the specifications described in this document. We will simply be extending the Kubernetes API using Custom Resource Definition as described here and then creating a custom controller that will handle the requirements of our provisioning Agent custom resource.
Overview of Proposed
...
Workflow for provisioning CRD
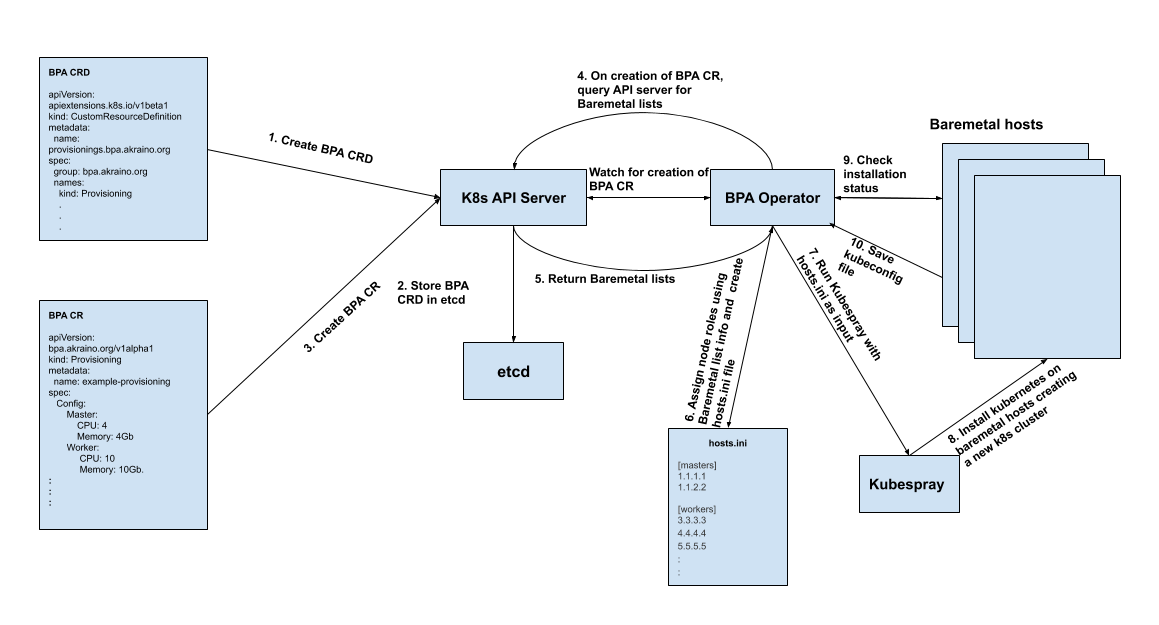
Prerequisites: This workflow assumes that the baremetal CR and baremetal operator have been created and has successfully installed the compute nodes with Linux OS. It also assumes that the BPA controller is running.
Fig 1: Illustration of the proposed workflow
...
- Create BPA CRD (Created only once and just creates the BPA resource kind)
Create the BPA Custom Resource
The BPA Operator continues to watch the k8s API server and once it sees that a new BPA CR object has been created, it queries the k8s API server for the Baremetal hosts lists. The baremetal hosts lists contains information about the compute nodes provisioned including the IP address, CPU, memory..etc of each host.
The BPA operator looks into the baremetal hosts list returned and decides on the roles of the compute nodes based on the CPU and memory (Other features may be added as we proceed). The resource requirements for master and worker nodes are defined in the BPA CR objecthosts list and knows which hosts should be master and which should be workers. As the master and worker fields have various parameters, it can do this in various ways;
- If the MAC address is provided in the BPA CR object, it compares that value with the value in the hosts list and assigns the roles. For example if a mac address of 00:c5:16:05:61:b2 is specified for master in the BPA CR spec, it checks the baremetal list for a host that has that MAC address and gives it the role of master.
- If there is no MAC address specified but just resources, it checks the baremetal list for hosts that meet the resource requirements
- If both MAC address and resource requirements are provided, it finds the host with the specified MAC address and confirms that the host meets the resource requirement provided in the BPA CR and then assigns the role.
- Using the MAC address of the host, the BPA operator looks in the DHCP file of the DHCP server running on the same host it is running and determines the IP address that corresponds to that MAC address
- The BPA operator reads a file containing the default username and password for the various hosts, copies its public key to those hosts in order to use kubespray later.
The BPA operator then creates the hosts.ini file using the assigned roles and their corresponding IP addresses.
The BPA operator then installs kubernetes using kubespray on the compute nodes thus creating an active kubernetes cluster. During installation, it would continue to check the status of the installation
On successful completion of the k8s cluster installation, the BPA operator would save the application-k8s kubeconfig file in order to access the k8s cluster and make changes such as software updates or add a worker node for future purposes.
...
Based on the values above, when the BPA operator gets the baremetal hosts object (Step 5in figure 1), it would assign hosts with 10 CPUs and 4Gi memory the role of master and it would assign hosts with 20CPUs and 8Gi memory the role of worker..
In addition, we would also have two other CRDs that the BPA would use to perform its functions;
- Software CRD
- Cluster CRD
Software CRD
The software CRD will install the required software, drivers and perform software updates
Cluster CRD
The CRD cluster will have the Cluster name and contain the provisioning CR and/or the software CR for the specified cluster
Open Questions
- How does the BPA operator get the SSH information of the compute hosts ?
...