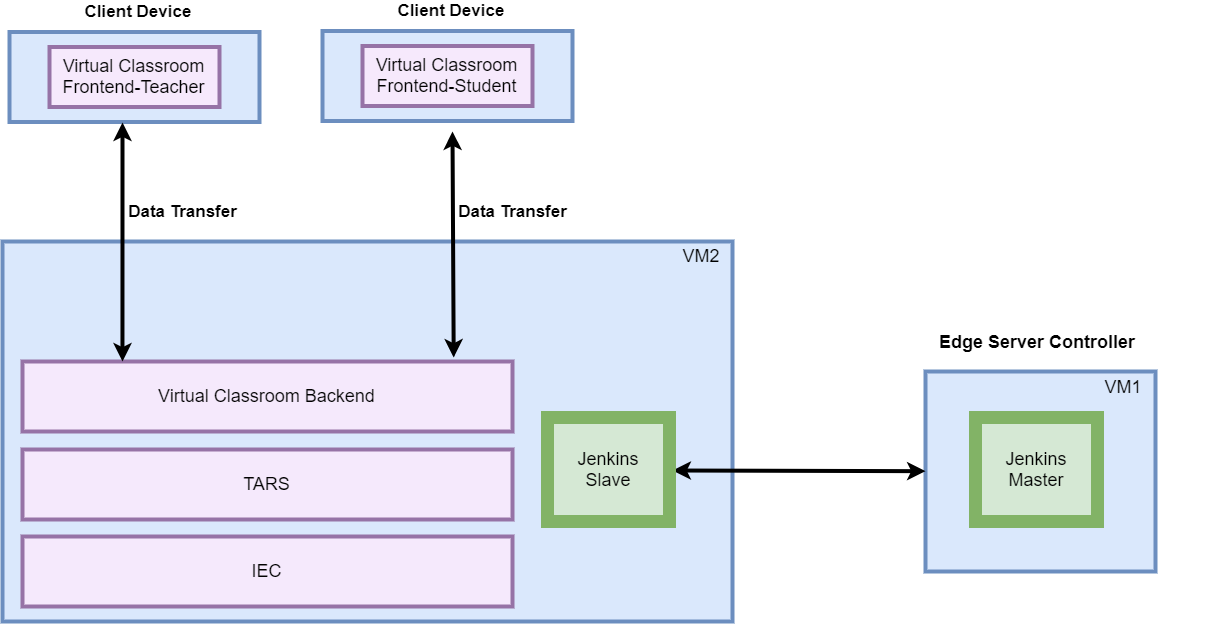
Deploy Architecture
To make the system deploy, the minimum deployment architecture is shown below, which consist of:
Hardware
- Wearable Glass (Optional)
- Teacher Client-Side — Personal Computer with Camera
- Student Client-Side — Personal Computer with Camera
- Server Side — 8 Core 16G Virtual Machine on ARM or x86 Platform
Software
- Teacher Side: Windows 10 with a Web Browser that supports WebSockets.
- Student Side: Windows 10 with a Web Browser that supports WebSockets.
- Server Side: CentOS 7
- Virtual Classroom
- Tars
- IEC
Installation on the Client PC side(Teacher/Student Client)
Note well: No special software to access the application. The general software is itemized below:
- Install Windows 10
- Install camera driver
- Install Firefox browser
Create two Virtual Machines in the Cloud
For Tencent Cloud, refer to the following link to apply new instance:
https://intl.cloud.tencent.com/document/product/213/9384?lang=en
For AWS A1, apply new instance, refer to the following link to apply new instance:
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/concepts.html
Installation on VM1(Jenkins Slave)
- Install CentOS 7, refer to https://phoenixnap.com/kb/how-to-install-centos-7
- Install IEC, refer to IEC Type1&2 Installation Guide for R2
- Install Tars, refer to https://github.com/TarsCloud/Tars/blob/master/Install.md
Install Virtual Classroom BackEnd
cd /root
yum install -y npm
yum install -y git
yum install -y docker
yum update -y
systemctl restart docker
sleep 3
npm install http-server -g
rm -rf openvidu-vr
git clone https://github.com/OpenVidu/openvidu-vr.git
cd /root/openvidu-vr/openvidu-vr-room/
sed -i 's/demos.openvidu.io/${Local_IP_Address}/g' app.js
sleep 3
docker run --rm --name openvidu_server -d -p 4443:4443 -e openvidu.secret=MY_SECRET -e openvidu.publicurl=https://${Local_IP_Address}:4443/ openvidu/openvidu-server-kms
sleep 6
- Install Java for Jenkins Slave
For Slave Mode, install Java will be ok.
sudo yum install -y java-1.8.0-openjdk-develInstallation on VM2(Jenkins Master)
Jenkins is a Java application, so the first step is to install Java. Run the following command to install the OpenJDK 8 package:
sudo yum install -y java-1.8.0-openjdk-devel
The next step is to enable the Jenkins repository. To do that, import the GPG key using the following curl command:
curl --silent --location http://pkg.jenkins-ci.org/redhat-stable/jenkins.repo | sudo tee /etc/yum.repos.d/jenkins.repo
And add the repository to your system with:
sudo rpm --import https://jenkins-ci.org/redhat/jenkins-ci.org.key
Once the repository is enabled, install the latest stable version of Jenkins by typing:
sudo yum install -y jenkins
After the installation process is completed, start the Jenkins service with:
sudo systemctl start jenkins
To check whether it started successfully run:
systemctl status jenkins
You should see something similar to this:
# systemctl status jenkins
* jenkins.service - LSB: Jenkins Automation Server
Loaded: loaded (/etc/rc.d/init.d/jenkins; bad; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since Tue 2019-10-15 11:16:26 CST; 1min 15s ago
Docs: man:systemd-sysv-generator(8)
Process: 489 ExecStart=/etc/rc.d/init.d/jenkins start (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
CGroup: /system.slice/jenkins.service
`-510 /etc/alternatives/java -Dcom.sun.akuma.Daemon=daemonized -Djava.awt.headless=true -DJENKINS_HOME=/var/lib/jenkins -jar /usr/l...
Oct 15 11:16:25 VM_0_4_centos systemd[1]: Starting LSB: Jenkins Automation Server...
Oct 15 11:16:26 VM_0_4_centos runuser[491]: pam_unix(runuser:session): session opened for user jenkins by (uid=0)
Oct 15 11:16:26 VM_0_4_centos runuser[491]: pam_unix(runuser:session): session closed for user jenkins
Oct 15 11:16:26 VM_0_4_centos jenkins[489]: Starting Jenkins [ OK ]
Oct 15 11:16:26 VM_0_4_centos systemd[1]: Started LSB: Jenkins Automation Server.
Finally enable the Jenkins service to start on system boot.
sudo systemctl enable jenkins
output
# sudo systemctl enable jenkins
jenkins.service is not a native service, redirecting to /sbin/chkconfig.
Executing /sbin/chkconfig jenkins on
Adjust the Firewall If you are installing Jenkins on a remote CentOS server that is protected by a firewall you need to port 8080.
Use the following commands to open the necessary port:
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-port=8080/tcp
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Setting Up Jenkins To set up your new Jenkins installation, open your browser and type your domain or IP address followed by port 8080:
http://your_ip_or_domain:8080
You will see the website itemized below:
Select the left option and install the plugin later:
I
Deploy Architecture
To make the system deploy, the minimum deployment architecture is shown below, which consist of:
Hardware
- Wearable Glass (Optional)
- Teacher Client-Side — Personal Computer with Camera
- Student Client-Side — Personal Computer with Camera
- Server Side — 8 Core 16G Virtual Machine on ARM or x86 Platform
Software
- Teacher Side: Windows 10 with a Web Browser that supports WebSockets.
- Student Side: Windows 10 with a Web Browser that supports WebSockets.
- Server Side: CentOS 7
- Virtual Classroom
- Tars
- IEC
Installation on the Client PC side(Teacher/Student Client)
Note well: No special software to access the application. The general software is itemized below:
- Install Windows 10
- Install camera driver
- Install Firefox browser
Create two Virtual Machines in the Cloud
For Tencent Cloud, refer to the following link to apply new instance:
https://intl.cloud.tencent.com/document/product/213/9384?lang=en
For AWS A1, apply new instance, refer to the following link to apply new instance:
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/concepts.html
Installation on VM1(Jenkins Slave)
- Install CentOS 7, refer to https://phoenixnap.com/kb/how-to-install-centos-7
- Install IEC, refer to IEC Type1&2 Installation Guide for R2
- Install Tars, refer to https://github.com/TarsCloud/Tars/blob/master/Install.md
Install Virtual Classroom BackEnd
cd /root
yum install -y npm
yum install -y git
yum install -y docker
yum update -y
systemctl restart docker
sleep 3
npm install http-server -g
rm -rf openvidu-vr
git clone https://github.com/OpenVidu/openvidu-vr.git
cd /root/openvidu-vr/openvidu-vr-room/
sed -i 's/demos.openvidu.io/${Local_IP_Address}/g' app.js
sleep 3
docker run --rm --name openvidu_server -d -p 4443:4443 -e openvidu.secret=MY_SECRET -e openvidu.publicurl=https://${Local_IP_Address}:4443/ openvidu/openvidu-server-kms
sleep 6
- Install Java for Jenkins Slave
For Slave Mode, install Java will be ok.
sudo yum install -y java-1.8.0-openjdk-develInstallation on VM2(Jenkins Master)
Jenkins is a Java application, so the first step is to install Java. Run the following command to install the OpenJDK 8 package:
sudo yum install -y java-1.8.0-openjdk-devel
The next step is to enable the Jenkins repository. To do that, import the GPG key using the following curl command:
curl --silent --location http://pkg.jenkins-ci.org/redhat-stable/jenkins.repo | sudo tee /etc/yum.repos.d/jenkins.repo
And add the repository to your system with:
sudo rpm --import https://jenkins-ci.org/redhat/jenkins-ci.org.key
Once the repository is enabled, install the latest stable version of Jenkins by typing:
sudo yum install -y jenkins
After the installation process is completed, start the Jenkins service with:
sudo systemctl start jenkins
To check whether it started successfully run:
systemctl status jenkins
You should see something similar to this:
# systemctl status jenkins
* jenkins.service - LSB: Jenkins Automation Server
Loaded: loaded (/etc/rc.d/init.d/jenkins; bad; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since Tue 2019-10-15 11:16:26 CST; 1min 15s ago
Docs: man:systemd-sysv-generator(8)
Process: 489 ExecStart=/etc/rc.d/init.d/jenkins start (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
CGroup: /system.slice/jenkins.service
`-510 /etc/alternatives/java -Dcom.sun.akuma.Daemon=daemonized -Djava.awt.headless=true -DJENKINS_HOME=/var/lib/jenkins -jar /usr/l...
Oct 15 11:16:25 VM_0_4_centos systemd[1]: Starting LSB: Jenkins Automation Server...
Oct 15 11:16:26 VM_0_4_centos runuser[491]: pam_unix(runuser:session): session opened for user jenkins by (uid=0)
Oct 15 11:16:26 VM_0_4_centos runuser[491]: pam_unix(runuser:session): session closed for user jenkins
Oct 15 11:16:26 VM_0_4_centos jenkins[489]: Starting Jenkins [ OK ]
Oct 15 11:16:26 VM_0_4_centos systemd[1]: Started LSB: Jenkins Automation Server.
Finally enable the Jenkins service to start on system boot.
sudo systemctl enable jenkins
output
# sudo systemctl enable jenkins
jenkins.service is not a native service, redirecting to /sbin/chkconfig.
Executing /sbin/chkconfig jenkins on
Adjust the Firewall If you are installing Jenkins on a remote CentOS server that is protected by a firewall you need to port 8080.
Use the following commands to open the necessary port:
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-port=8080/tcp
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Setting Up Jenkins To set up your new Jenkins installation, open your browser and type your domain or IP address followed by port 8080:
http://your_ip_or_domain:8080
You will see the website itemized below:
Select the left option and install the plugin later: