...
The Mobile Edge deployments can will provide APIs to support below capabilities such as the following:
- UPF Distribution/Shunting capability -- distributing User Plane Functions in the appropriate Data Center Facilities on qualified compute hardware for routing the traffic to desired applications and network/processing functions/applications.
- Local Break-Out (LBO) – Examples: video traffic offload, low latency services, roaming optimization.
- Location Services -- the location of a specific UE, or identification of UEs within a geographical area, facilitation of server-side application workload distribution based on UE and infrastructure resource location.
- QoS acceleration/extension – provide low latency, high throughput for Edge applications. Example: provide continuity for QoS provisioned for subscribers in the MNO domain, across the interconnection/networking domain for end-to-end QoS functionality.
- Network Slicing provisioning and and management - providing continuity for network slices instantiated in the MNO domain, across the Public Cloud Core/Edge as well as the 3Rd-Party Edge domains, offering dedicated resources specifically tailored for application and functional needs (e.g. security) needs.
- Mobile Hybrid/Multi-Cloud Access - provide multi-MNO, multi-Cloud, multi-MEC access for mobile devices (including IoT) and Edge services/applications
- Enterprise Wireless WAN access - provide high-speed Fixed Wireless Access to enterprises with the ability to interconnect to Public Cloud and 3rd-Party Edge Functions, including the Network Functions such as SD-WAN.
- Authentication – provide service enablement (e.g., two-factor authentication) used by most OTT service providers
- Security – provide service enablement (e.g., firewall service insertion)
...
Public Cloud Service Providers and 3rd-Party MEC Providers are deploying Edge instances to better serve their end-users and applications, A multitude of these applications require close inter-working with the MNO Edge deployments to provide predictable latency & throughput, reliability, and other telco-grade requirements. The purpose of this blueprint family is to specify a standard set of APIs to expose towards Public Cloud and 3rd-Party MEC Service Provider instances at the Edge.
The need to interface and exchange information through these open APIs will allow competitive offerings for Consumers, Enterprises, and Vertical Industry end-user segments. For instance, open APIs will be provided between Telcos and public cloud edge compute platforms such as Google Cloud Platform (GCP) Anthos, AliCloud Edge Node Service (ENS), AWS Wavelength, Microsoft Azure Edge Zones, Tencent ECM, to name a few. These APIs are not limited to providing basic connectivity services but will include the ability to deliver predictable data rate, predictable latency, reliability, service insertion, security, AI and RAN analytics, network slicing, and more. These capabilities are needed to support a multitude of emerging applications such as AR/VR, Industrial IoT, autonomous vehicles, drones, Industry 4.0 initiatives, Smart Cities, Smart Ports. Other APIs will include exposure to edge orchestration and management, Edge monitoring (KPIs), and more. These open APIs will be the foundation for service and instrumentation APIs when integrating with public cloud development environments and will be defined as part of the implementation. Even though these APIs will be common across all Telco operators, the differentiation will based on services provided through those APIs.
...
Note that as part of the Southbound capabilities, there is a need for APIs exposed by the Data Center providers, Bare-Metal Hardware Orchestration providers as well as the Interconnection providers in order to facilitate distribution of processing resources as well as the interconnection between multiple entities providing/consuming Edge services/applications.
...
The Mobile Network Operator (MNO) Domain. The MNO Domain contains all Access and Core Network Functions necessary for signalling signaling and user plane capabilities to allow for mobile device connectivity. These functions include the Radio Access Network (RAN), including the 5G New RAN (5GNR), Packet Core, including the Virtualized Evolved Packet Core (vEPC) and the 5G Core (5GC).
The Public Cloud Core (PCC) Domain. The PCC Domain includes all IaaS/PaaS functions that are provided by the Public Clouds cloud to their customers. These include Virtual Private Cloud and Public/Private Networking capabilities.
...
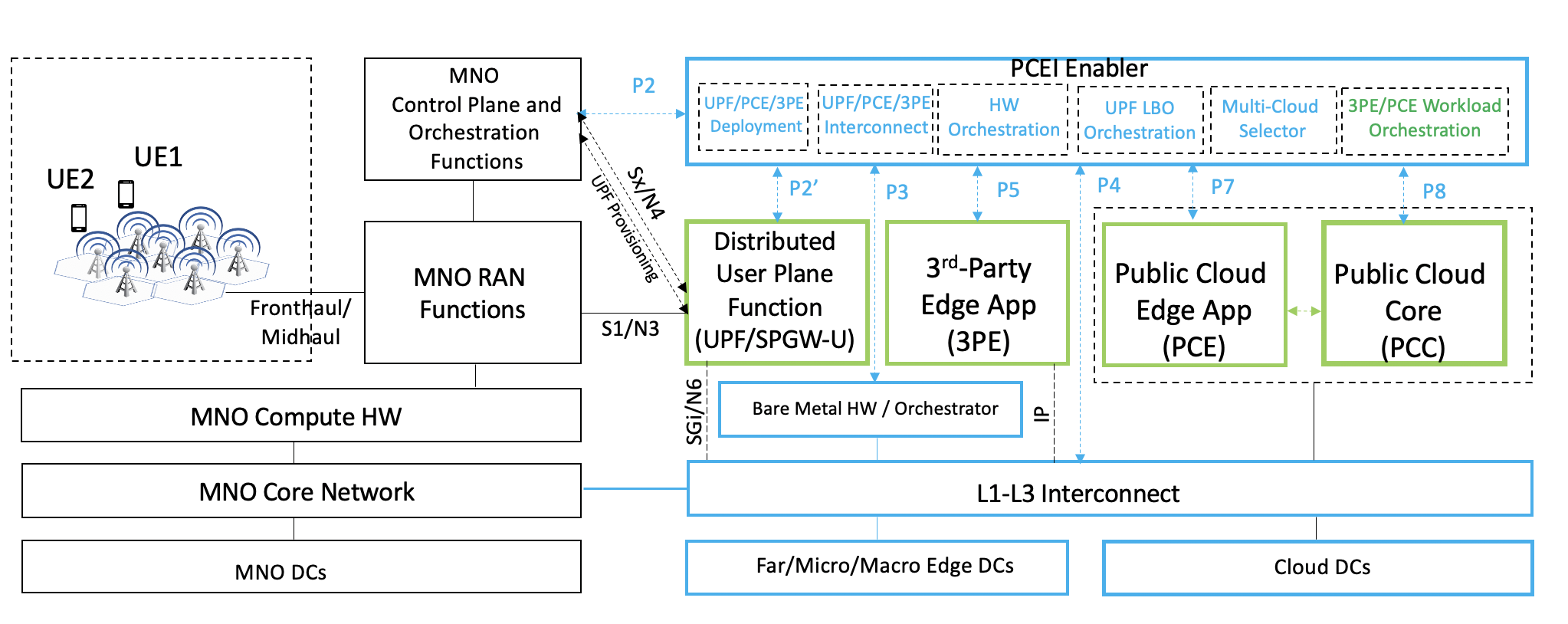
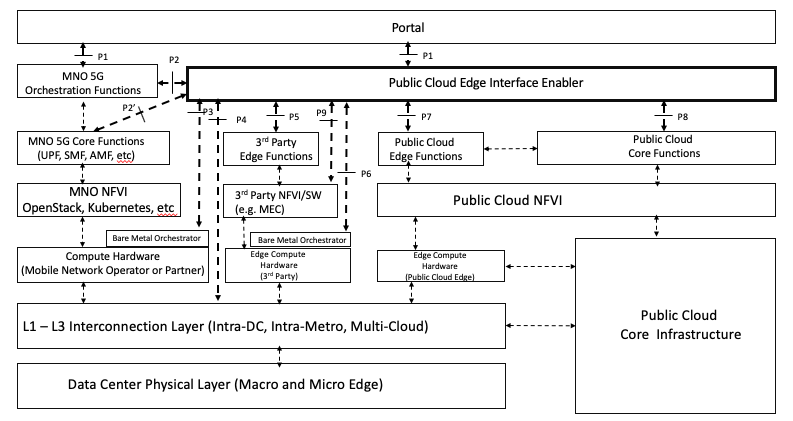
The PCEI Reference Architecture and the Interface Reference Points (IRP) are shown in the figure figures below. Note the this figure also provides a component layer view of the PCEI Architecture:
Figure 3a. The PCEI Summary Reference Architecture.
Figure 33b. The PCEI Detailed Reference Architecture.
The PCEI Reference Architecture layers are described below:
...
- Compute Hardware. This includes Compute, Network and Storage resources that support MNO functions. Note that the PCEI Reference Architecture recognizes a model, where a an MNO has the ability to distribute the compute infrastructure in appropriate locations in the DCF Domain in order to satisfy performance and functional requirements for the targeted application use cases. For example, a an MNO may wish to implement a Local Break-Out (LBO) in locations that are geographically closer to the mobile subscribers , and uses compute hardware provided by a qualified Bare Metal service provider.
- The PCEI Architecture further recognizes a model, where the Compute Hardware layer is accessible via the Bare Metal Orchestrator that enables dynamic instantiation of compute/network resources for the MNO functions.
- Network Function Virtualization Infrastructure (NFVI). This is the virtualization layer (e.g. OpenStack, Kubernetes) that may be specific to MNO requirements and provides the ability to support MNO functions such as the 5GC User Plane Function (UPF).
- MNO Core Functions. This layer corresponds to the key MNO Core functions applicable to the PCEI. These functions include (but not limited to): UPF, SMF and other applicable 4G vEPC and 5G Core functions.
- MNO Orchestration Functions. These functions are responsible for communicating the MNO service/performance requirements to the PCEI Enabler and for orchestrating services within the MNO Domain. Examples of these functions include NSSF, NRF, etc.
...
- Public Cloud Core Infrastructure. This includes all IaaS/PaaS functions that are provided by the Public Clouds cloud to their customers. These include Virtual Private Cloud and Public/Private Networking capabilities.
- Public Cloud Edge Compute Hardware. This is Compute, Network, and Storage resources that support PCE functions. The PCE compute hardware is usually a vertically integrated hardware resource set controlled by the PCC Infrastructure and connected to it by means of of the L1-L3 Interconnection layer.
- Public Cloud NFVI. This is the virtualization layer specific to the Public Cloud service provider.
- Public Cloud Core Functions. These functions are the specific capabilities offered by the Public Cloud service provider to its customers. Examples include Virtual Public Cloud (and equivalents), Virtual and Physical Private Networking.
- Public Cloud Edge Functions. A set of Public Cloud resources executing on PCE hardware and controlled by the PCC functions.
...
- Compute Hardware. This includes Compute, Network, and Storage resources that support 3PE functions. Note that the PCEI Reference Architecture recognizes a model, where a 3rd Party provider has the ability to distribute the compute infrastructure in appropriate locations in the DCF Domain in order to satisfy performance and functional requirements for the targeted application use cases. For example, an online gaming provider may wish to implement their services in locations that are geographically closer to the mobile online gaming subscribers, and uses use compute hardware provided by a qualified Bare Metal service provider.
- The PCEI Architecture further recognizes a model, where the Compute Hardware layer is accessible via the Bare Metal Orchestrator that enables dynamic instantiation of compute/network resources for the 3PE functions.
- 3rd Party Edge NFVI layer. These are the NFVI software and capabilities needed to support functionality such as the Multi-Access Edge Computing (MEC).
- 3rd Party Edge Functions. These are edge computing application functions including the Network Functions (NFVs, e.g. SD-WAN, vFW, vRouter) and the Processing Functions (e.g. CDN Cache, IoT Gateways, AI Inferencing Model).
...
The PCEI Portal. An optional component of the PCEI Architecture responsible for providing the users of PCEI a way to express and communicate their intended functional, performance, and service requirements.
...
P2 – Interface between PCEI and Mobile Network. Provides the ability to accept requests from MNO for PCEI service and request MNO to provide 4G/5G access to PCEI customers. E.g. Network Slicing, LBO.
P2' - Interface between PCEI and the MNO Core Functions such as UPF, SMF. In case of a UPF the P2' interface can be used to configure the the parameters responsible for interfacing the UPF and the virtual/contextual configuration structures within the UPF with the PCC/PCE and 3PE resources by way of the L1-L3 Interconnection layer. The P2' interface implies the availability of standard or well-specified UPF provisioning models provided by MNOs.
...
P4 – Interface between PCEI and Interconnection Fabric. Provides ability abilities to request and orchestrate network connectivity and performance KPIs between MNO UPF, Cloud Core and Edge resources (including 3rd Party Edge)
P5 – Interface between PCEI and 3rd Party Edge Functions (e.g. NFV). Provides ability abilities to access Edge APIs exposed by 3rd Party Edge Functions (e.g. deployment of NFVs and Edge Processing workloads)
P6 – Interface between PCEI and Edge Compute Hardware Orchestrator. Provides the ability for PCEI to trigger orchestration of appropriate HW resources for Edge Compute functions including Public Cloud Edge and 3rd party Edge.
P7 – Interface between PCEI and Public Cloud Edge Functions (may be maybe part of P8). Provides ability abilities to access APIs to deploy Public Cloud Edge functions/Instances (may be done through P8)
P8 - Interface between PCEI and Public Cloud Core Functions (may include control over Public Cloud Edge functions). Provides the ability to access Public Cloud APIs including the ability to deploy Public Cloud edge functions.
P9 - Interface between PCEI and the NFVI layer of the 3PE Domain. P9 may be used If a an MNO chooses to expose the NFVI layer to PCEI.
Software Platform Architecture
<Software components with version/release numbers >
<EDGE Interface>
<ETSI MEC Interaction>
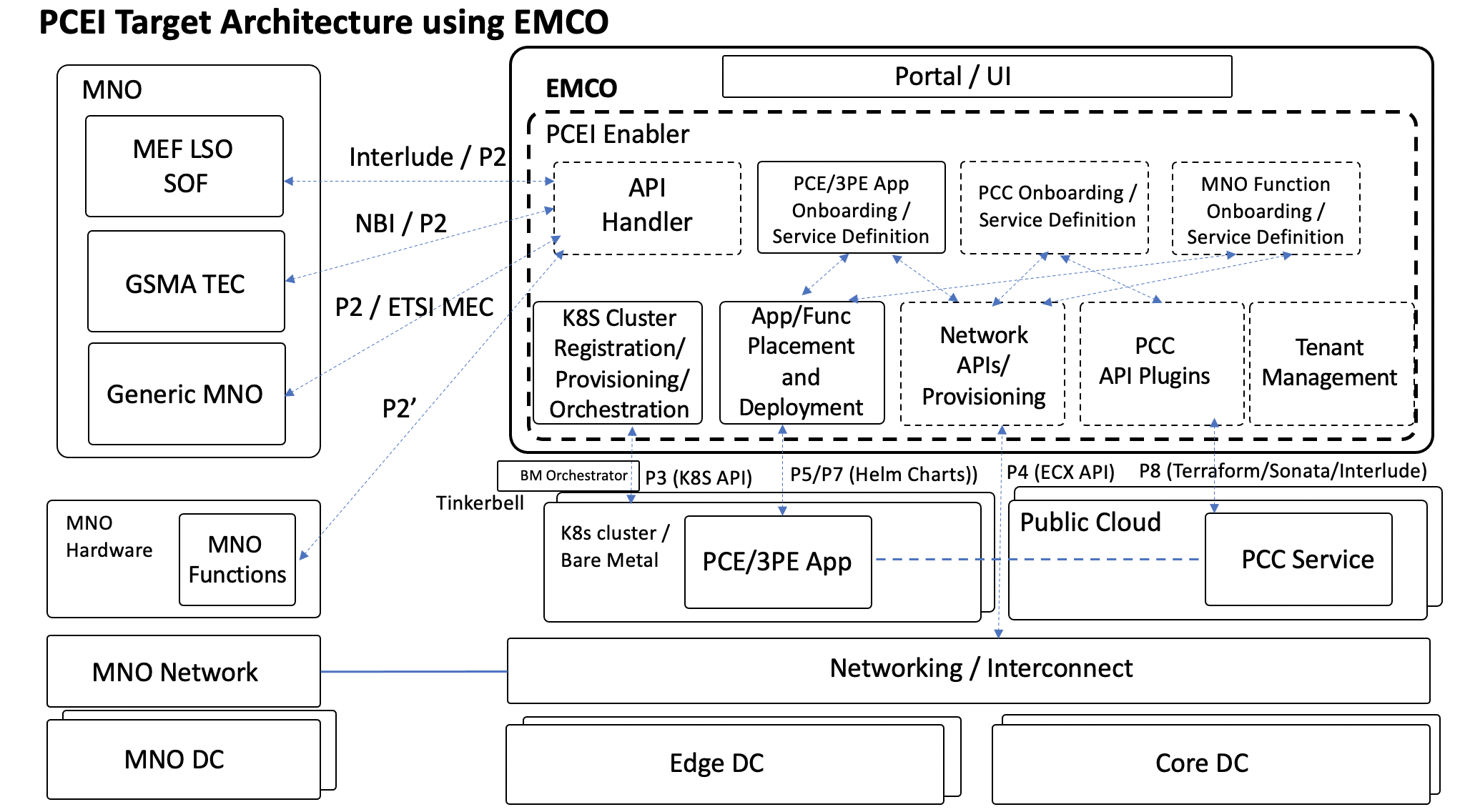
PCEI Enabler is based on EMCO - Edge Multi-Cluster Orchestrator:
https://wiki.onap.org/pages/viewpage.action?pageId=84668166
The target software architecture The general structure of the PCEI Enabler based on EMCO is shown below:. Note that all references to specific APIs and SDOs are for mapping purposes only, subject to ongoing analysis and do not indicate compliance with APIs/SDO specs.
Figure 4. General structure of PCEI Enabler.
...
APIs with reference to Architecture and Modules
High-Level definition of APIs are stated here, assuming Full definition APIs are in the API documentation
...