Contents
CICD Orchestration
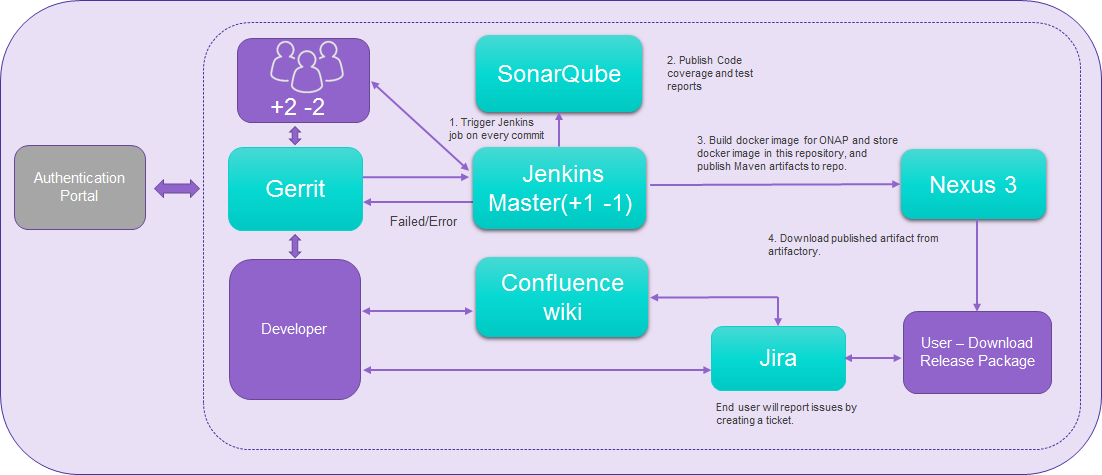
The following diagram illustrates the Akraino CI/CD components:
Gerrit is used to help eliminate or drastically reduce the chance of problematic code entering Akraino. Gerrit allows for developers to push proposed, much-focused changes, automatically triggering a peer review workflow. Jenkins partakes in this workflow as well (via the Jenkins Gerrit Trigger plugin), performing any necessary tests, including static code analysis and unit tests, reporting back to Gerrit with the results. Another peer review may occur in tandem, though it is usually recommended to wait for Jenkins to vote on the proposed change first.
The combination of Gerrit and Jenkins allows for independent, automated code review prior to merging. Developers push proposed code changes to a Gerrit review branch instead of the anticipated target branches. In fact, pushing to the target branches is not allowed. All proposed changes must be sent through the Gerrit workflow, which Jenkins partakes in.
While there are automated workflow steps, it is considered proper Gerrit etiquette for contributors to run all available analysis and tests on the development workstation. In this way, Jenkins in particular acts as more of a safety net, including any additional checks that may only be performed remotely. This also reduces the number of Gerrit patch sets and is more considerate of peer reviewer’s time.
Overview of Akraino CD Process
Herewith are the configuration steps used to achieve a Continuous Deployment setup (Webhook), when committing to Gerrit:
- Configure Jenkins as a Continuous Integration tool that will receive the hook from Gerrit.
Once the developer commits the code in Gerrit, the respective Jenkins jobs will trigger, running the build and test steps.
Once the build and test steps complete, the respective unit test case results (pass/fail) will be posted to SonarQube.
- If the job is successful per Jenkins job instructions, it will create JAR/WAR files and Docker containers, then post them to the Nexus3 repo.
CD Environment for Akraino Seed Code
Akraino Seed Code is in Linux Foundation Nexus, currently available to TSC as of this writing. All authorized developers will be granted commit access to Linux Foundation Gerrit. Developers are required to build JJB templates for their projects to integrate with Linux Foundation Jenkins. Code Reviewers will be assigned to review and approve the code commits to merge. Version control is employed to allow developers to choose the specific version. The latest version is the default.
Akraino CD is integrated with Akraino CI in Linux Foundation. The Peer Jenkins is established in the Akraino CD environment, and it communicates with Linux Foundation Gerrit. Peer Jenkins is setup to download repos from Linux Foundation Nexus on a daily basis for a complete CD install. The Peer Jenkins uploads the logs generated from the full CD run to the log server in Nexus.