Overview
The purpose of this blueprint is an end-to-end technology solution for mobile game deployed across multiple heterogeneous edge nodes using various network access protocols such as mobile and WiFi and others. This blueprint demonstrates how an application leverages a distributed and multi access network edge environment in order to get all the benefits of edge computing.
This is the very first release of this new blueprint as part of the Akraino PCEI family. Current focus for this release is to enable open source Karmada based cloud federation & kubeEdge/EdgeMesh based East-West networking functionality.
Multi-cluster Management
Environmental Information (CentOS8.0 4U8G)
Username & Password: root/Akraino2021
CPU Name | Role | IP | Workload |
|---|---|---|---|
kubeedge-karamda-001 | Karmada Control Plane | 159.138.22.176 | Karmada controllers, karmada api |
kubeedge-karamda-002 | Cluster02 | 182.160.12.59 | K8s, docker |
kubeedge-karamda-003 | Cluster01 | 159.138.43.243 | K8s, docker |
Deployment Manual
Karmada control plane deployment
Disable boot firewall
# systemctl disable firewalld
Install Docker
# yum install wget container-selinux -y
# yum erase runc -y
# rpm -ivh containerd.io-1.2.6-3.3.el7.x86_64.rpm
Note: The above steps do not need to be operated in centos7
# update-alternatives --set iptables /usr/sbin/iptables-legacy
# yum install -y yum-utils device-mapper-persistent-data lvm2 && yum-config-manager --add-repo https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo && yum makecache
# yum -y install docker-ce
# systemctl enable docker.service && systemctl start docker
- Install Kind
# curl –Lo ./kind https://kind.sigs.k8s.io/d1/v0.10.0/kind-linux-amd64
# chmod +x ./kind
# mv ./kind /usr/local/bin/kind
# kind version
Install Go and configure the Golang environment
# wget https://golang.google.cn/dl/go1.17.0.linux-amd64.tar.gz
# tar –zxvf go1.17.0.linux-amd64.tar.gz –C /usr/local
# vi /etc/profile
Add at the end of file:
# golang env
export GOROOT=/usr/local/go
export GOPATH=/data/gopath
export PATH=$PATH:$GOROOT/bin:$GOPATH/bin
# source /etc/profile
# mkdir -p /data/gopath && cd /data/gopath
# mkidr –p src pkg bin
Configure yum source
# cat <<EOF > /etc/yum.repos.d/kubernetes.repo
[kubernetes]
name=Kubernetes
baseurl=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/repos/kubernetes-el7-x86_64
enabled=1
gpgcheck=1
repo_gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/yum-key.gpg https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/rpm-package-key.gpg
EOF
Install KubeCtl
# yum makecache
# yum instal –y kubectl
Install Karmada control plane components
# git clone https://github.com/karmada-io/karmada
# cd karmada
# hack/local-up-karmada.sh
Edge cluster deployment
Disable boot firewall
# systemctl disable firewalld
Install Docker
# yum install wget container-selinux -y
# yum erase runc -y
# rpm -ivh containerd.io-1.2.6-3.3.el7.x86_64.rpm
Note: The above steps do not need to be operated in centos7
# update-alternatives --set iptables /usr/sbin/iptables-legacy
# yum install -y yum-utils device-mapper-persistent-data lvm2 && yum-config-manager --add-repo https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo && yum makecache
# yum -y install docker-ce
# systemctl enable docker.service && systemctl start docker
Configure yum source
[root@kubeEdge-cloud ~]# cat <<EOF > /etc/yum.repos.d/kubernetes.repo
[kubernetes]
name=Kubernetes
baseurl=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/repos/kubernetes-el7-x86_64
enabled=1
gpgcheck=1
repo_gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/yum-key.gpg https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/rpm-package-key.gpg
EOF
Install KubeAdm, KubeCtl
# yum makecache
# yum install kubelet-1.21.0-0.x86_64 kubeadm-1.21.0-0.x86_64 kubectl-1.21.0-0.x86_64
Configure the kernel parameters
[root@kubeEdge-cloud ~]# cat <<EOF > /etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1
vm.swappiness=0
EOF
[root@kubeEdge-cloud ~]# sysctl --system
[root@kubeEdge-cloud ~]# modprobe br_netfilter
[root@kubeEdge-cloud ~]# sysctl -p /etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf
Load ipvs related kernel modules
If you reboot, you need to reload (it can be written in /etc/rc.local to automatically load at boot)
[root@ke-cloud ~]# modprobe ip_vs
[root@ke-cloud ~]# modprobe ip_vs_rr
[root@ke-cloud ~]# modprobe ip_vs_wrr
[root@ke-cloud ~]# modprobe ip_vs_sh
[root@ke-cloud ~]# modprobe nf_conntrack_ipv4
Check whether the loading is successful
[root@ke-cloud ~]# lsmod | grep ip_vs
Pull Mirror
[root@kubeEdge-cloud ~]# kubeadm config images list
[root@kubeEdge-cloud ~]# kubeadm config images pull
Install Kubelet
1)Get docker cgroups
# DOCKER_CGROUPS=$(docker info | grep 'Cgroup Driver' | cut -d' ' -f4)
# echo $DOCKER_CGROUPS
cgroupfs
2)Configure cgroups for kubelet
# cat >/etc/sysconfig/kubelet<<EOF
KUBELET_EXTRA_ARGS="--cgroup-driver=$DOCKER_CGROUPS --pod-infra-container-image=k8s.gcr.io/pause:3.5"
EOF
3)Start kubelet
# systemctl daemon-reload
# systemctl enable kubelet && systemctl start kubelet
Initialize the cluster
# kubeadm init --kubernetes-version=v1.17.9 \
--pod-network-cidr=10.244.0.0/16 \
--apiserver-advertise-address=192.168.0.238 \
--ignore-preflight-errors=Swap
Install network plugin
1)Download the yaml file of flannel plug-in.
# cd ~ && mkdir flannel && cd flannel
# curl -O https://raw.githubusercontent.com/coreos/flannel/master/Documentation/kube-flannel.yml
2)Startup
# kubectl apply -f ~/flannel/kube-flannel.yml
Log in to the karmada-host node and join the multi-cluster (the karmada.config below refers to the kubeconfig of the existing k8s cluster)
# hack/create-cluster.sh member1 $HOME/.kube/karmada.config
# go get github.com/karmada-io/karmada/cmd/karmadactl
# karmadactl join cluster01--cluster-kubeconfig=$HOME/.kube/karmada.config
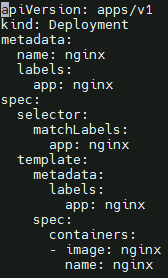
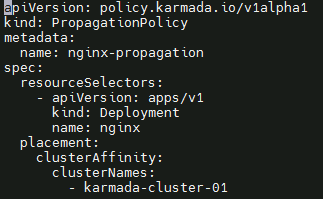
Nginx application deployment
- Create nginx deployment
Create the nginx propagation policy
East-West Edge-to-Edge Networking
Environmental Information (CentOS8.0 4U8G)
Username & Password: root/Akraino2021
CPU Name | Role | IP | Workload |
|---|---|---|---|
Kubeedge-akraino-0001 | Cloud | 159.138.149.190 | K8S, docker, cloudcore |
Kubeedge-akraino-0002 | Edge Node | 119.8.35.111 | docker, edgecore, edgemesh |
Kubeedge-akraino-0003 | Edge Node | 182.160.10.130 | docker, edgecore, edgemesh |
Deployment Manual
Deploy cloud nodes (kubeEdge-cloud)
Disable boot firewall
# systemctl disable firewalld
Install Docker
# yum install wget container-selinux -y
# yum erase runc -y
# rpm -ivh containerd.io-1.2.6-3.3.el7.x86_64.rpm
Note: The above steps do not need to be operated in centos7
# update-alternatives --set iptables /usr/sbin/iptables-legacy
# yum install -y yum-utils device-mapper-persistent-data lvm2 && yum-config-manager --add-repo https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo && yum makecache
# yum -y install docker-ce
# systemctl enable docker.service && systemctl start docker
Configure yum source
[root@kubeEdge-cloud ~]# cat <<EOF > /etc/yum.repos.d/kubernetes.repo
[kubernetes]
name=Kubernetes
baseurl=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/repos/kubernetes-el7-x86_64
enabled=1
gpgcheck=1
repo_gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/yum-key.gpg https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/rpm-package-key.gpg
EOF
Install Kubeadm, kubectl
# yum makecache
# yum install kubelet-1.21.0-0.x86_64 kubeadm-1.21.0-0.x86_64 kubectl-1.21.0-0.x86_64
Note: The current KubeEdge version does not match the 1.22 version of K8s, and the latest version cannot be installed.
Configure the kernel parameters
[root@kubeEdge-cloud ~]# cat <<EOF > /etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1
vm.swappiness=0
EOF
[root@kubeEdge-cloud ~]# sysctl --system
[root@kubeEdge-cloud ~]# modprobe br_netfilter
[root@kubeEdge-cloud ~]# sysctl -p /etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf
Load ipvs related kernel modules
If you reboot, you need to reload (it can be written in /etc/rc.local to automatically load at boot)
[root@ke-cloud ~]# modprobe ip_vs
[root@ke-cloud ~]# modprobe ip_vs_rr
[root@ke-cloud ~]# modprobe ip_vs_wrr
[root@ke-cloud ~]# modprobe ip_vs_sh
[root@ke-cloud ~]# modprobe nf_conntrack_ipv4
Check whether loading is successful
[root@ke-cloud ~]# lsmod | grep ip_vs
Pull Mirror
[root@kubeEdge-cloud ~]# kubeadm config images list
[root@kubeEdge-cloud ~]# kubeadm config images pull
Initialize the cluster
[root@ke-cloud ~]# kubeadm init --kubernetes-version=v1.17.9 \
--pod-network-cidr=10.244.0.0/16 \
--apiserver-advertise-address=192.168.0.238 \
--ignore-preflight-errors=Swap
Deploy Cloudcore
Prerequisites: install golang
[root@kudeEdge-cloud ~]# git clone https://github.com/kubeedge/kubeedge $GOPATH/src/github.com/kubeedge/kubeedge
[root@kudeEdge-cloud ~]# cd $GOPATH/src/github.com/kubeedge/kubeedge
[root@kudeEdge-cloud ~]# make all WHAT=keadm
[root@kudeEdge-cloud ~]# keadm init --advertise-address="192.168.0.238"
Deploy edge nodes (edgemesh version is release1.7)
- Install docker same as before
- Obtain the token on the cloud node
[root@kudeEdge-cloud ~]# keadm gettoken
- Install edgecore and mqtt
[root@kudeEdge-cloud ~]# keadm join --cloudcore-ipport=192.168.1.66:10000 --token=“上一步骤获取的token”
--token="token obtained in the previous step"
- Modify the edgecore configuration
[root@kudeEdge-cloud ~]# vim /etc/kubeedge/config/edgecore.yaml
modules:
..
edgeMesh:
enable: false
metaManager:
metaServer:
enable: true
..
- Restart edgecore
[root@kudeEdge-cloud ~]# systemctl restart edgecore
- Modify cloudcore configuration and restart cloudcore
[root@kudeEdge-cloud ~]# vim /etc/kubeedge/config/cloudcore.yaml
modules:
..
dynamicController:
enable: true
..
- Pull EdgeMesh code and build EdgeMesh image
[root@kudeEdge-cloud ~]# docker build -t edgemesh:0.1 -f build/Dockerfile .
- Deploy EdgeMesh
Modify the following configuration file, modify service-cluster-ip-range.
[root@kudeEdge-cloud ~]# kubectl apply -f build/kubernetes/edgemesh/03-configmap.yaml
[root@kudeEdge-cloud ~]# kubectl apply -f build/kubernetes/edgemesh/04-daemonset.yaml
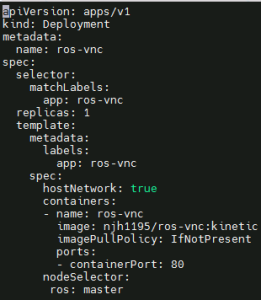
Deploy ROS application
Create ros-deployment-master.yaml and deploy
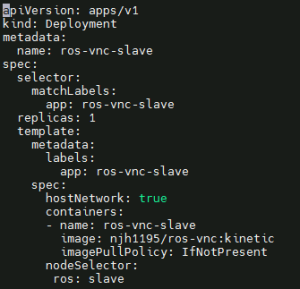
Create ros-deployment-slave.yaml and deploy
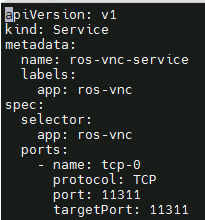
Create ros-master-service.yaml and deploy
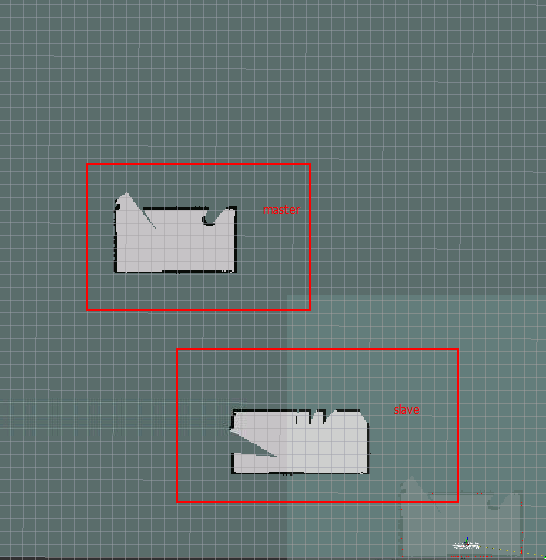
ros application master node operation
Open the master node page, http://182.160.10.130:80
Refer to the operation of https://hub.docker.com/r/njh1195/ros-vnc:
- Open the terminal page and execute "roscore" to start roscore
- Open the second terminal page and execute "roslaunch turtlebot3_gazebo multi_turtlebot3.launch”
- multi_turtlebot3.launch" to start three simulation robots
- Open the third terminal page and execute "ROS_NAMESPACE=tb3_0 roslaunch
- turtlebot3_slam turtlebot3_gmapping.launch set_base_frame:=tb3_0/base_footprint set_odom_frame:=tb3_0/odom set_map_frame:=tb3_0/map”, set_map_frame:=tb3_0/map" to start the first robot scan on the master node.
Open the fourth terminal page and execute "roslaunch turtlebot3_gazebo
multi_map_merge.launch" to open the merge program.
Generate a point source map and execute "rosrun rviz rviz -d `rospack find
- turtlebot3_gazebo`/rviz/multi_turtlebot3_slam.rviz”
ros application master node operation
Open the slave node page, http://159.138.49.1:80
Refer to the operation of https://hub.docker.com/r/njh1195/ros-vnc:
- Open the terminal page and configure ros-master's access service. The file is in /root/.bashrc.
Add the following configuration at the end of the file to configure the master access address and slave address:
- Open the second terminal page and execute "ROS_NAMESPACE=tb3_1 roslaunch
- turtlebot3_slam turtlebot3_gmapping.launch
set_base_frame:=tb3_1/base_footprint set_odom_frame:=tb3_1/odom
set_map_frame:=tb3_1/map", open the graphic scan of another room.
- Check whether the point source graph is Merged in the master node.