...
CPU Name | Role | IP | Workload |
|---|---|---|---|
kubeedge-karamda-001 | Karmada Control Plane | 159.138.22.176 | Karmada controllers, karmada api |
kubeedge-karamda-002 | Cluster02 | 182.160.12.59 | K8s, docker |
kubeedge-karamda-003 | Cluster01 | 159.138.43.243 | K8s, docker |
Deployment Manual
Karmada control plane deployment
Disable boot firewall
# systemctl disable firewalld
Install Docker
# yum install wget container-selinux -y
# yum erase runc -y
# rpm -ivh containerd.io-1.2.6-3.3.el7.x86_64.rpm
Note: The above steps do not need to be operated in centos7
# update-alternatives --set iptables /usr/sbin/iptables-legacy
# yum install -y yum-utils device-mapper-persistent-data lvm2 && yum-config-manager --add-repo https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo && yum makecache
# yum -y install docker-ce
# systemctl enable docker.service && systemctl start docker
- Install Kind
# curl –Lo ./kind https://kind.sigs.k8s.io/d1/v0.10.0/kind-linux-amd64
# chmod +x ./kind
# mv ./kind /usr/local/bin/kind
# kind version
Install Go and configure the Golang environment
# wget https://golang.google.cn/dl/go1.17.0.linux-amd64.tar.gz
# tar –zxvf go1.17.0.linux-amd64.tar.gz –C /usr/local
# vi /etc/profile
Add at the end of file:
# golang env
export GOROOT=/usr/local/go
export GOPATH=/data/gopath
export PATH=$PATH:$GOROOT/bin:$GOPATH/bin
# source /etc/profile
# mkdir -p /data/gopath && cd /data/gopath
# mkidr –p src pkg bin
Configure yum source
# cat <<EOF > /etc/yum.repos.d/kubernetes.repo
[kubernetes]
name=Kubernetes
baseurl=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/repos/kubernetes-el7-x86_64
enabled=1
gpgcheck=1
repo_gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/yum-key.gpg https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/rpm-package-key.gpg
EOF
Install KubeCtl
# yum makecache
# yum instal –y kubectl
Install Karmada control plane components
# git clone https://github.com/karmada-io/karmada
# cd karmada
# hack/local-up-karmada.sh
Edge cluster deployment
Disable boot firewall
# systemctl disable firewalld
Install Docker
# yum install wget container-selinux -y
# yum erase runc -y
# rpm -ivh containerd.io-1.2.6-3.3.el7.x86_64.rpm
Note: The above steps do not need to be operated in centos7
# update-alternatives --set iptables /usr/sbin/iptables-legacy
# yum install -y yum-utils device-mapper-persistent-data lvm2 && yum-config-manager --add-repo https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo && yum makecache
# yum -y install docker-ce
# systemctl enable docker.service && systemctl start docker
Configure yum source
[root@kubeEdge-cloud ~]# cat <<EOF > /etc/yum.repos.d/kubernetes.repo
[kubernetes]
name=Kubernetes
baseurl=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/repos/kubernetes-el7-x86_64
enabled=1
gpgcheck=1
repo_gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/yum-key.gpg https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/rpm-package-key.gpg
EOF
Install KubeAdm, KubeCtl
# yum makecache
# yum install kubelet-1.21.0-0.x86_64 kubeadm-1.21.0-0.x86_64 kubectl-1.21.0-0.x86_64
Configure the kernel parameters
[root@kubeEdge-cloud ~]# cat <<EOF > /etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1
vm.swappiness=0
EOF
[root@kubeEdge-cloud ~]# sysctl --system
[root@kubeEdge-cloud ~]# modprobe br_netfilter
[root@kubeEdge-cloud ~]# sysctl -p /etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf
Load ipvs related kernel modules
If you reboot, you need to reload (it can be written in /etc/rc.local to automatically load at boot)
[root@ke-cloud ~]# modprobe ip_vs
[root@ke-cloud ~]# modprobe ip_vs_rr
[root@ke-cloud ~]# modprobe ip_vs_wrr
[root@ke-cloud ~]# modprobe ip_vs_sh
[root@ke-cloud ~]# modprobe nf_conntrack_ipv4
Check whether the loading is successful
[root@ke-cloud ~]# lsmod | grep ip_vs
Pull Mirror
[root@kubeEdge-cloud ~]# kubeadm config images list
[root@kubeEdge-cloud ~]# kubeadm config images pull
Install Kubelet
1)Get docker cgroups
# DOCKER_CGROUPS=$(docker info | grep 'Cgroup Driver' | cut -d' ' -f4)
# echo $DOCKER_CGROUPS
cgroupfs
2)Configure cgroups for kubelet
# cat >/etc/sysconfig/kubelet<<EOF
KUBELET_EXTRA_ARGS="--cgroup-driver=$DOCKER_CGROUPS --pod-infra-container-image=k8s.gcr.io/pause:3.5"
EOF
3)Start kubelet
# systemctl daemon-reload
# systemctl enable kubelet && systemctl start kubelet
Initialize the cluster
# kubeadm init --kubernetes-version=v1.17.9 \
--pod-network-cidr=10.244.0.0/16 \
--apiserver-advertise-address=192.168.0.238 \
--ignore-preflight-errors=Swap
Install network plugin
1)Download the yaml file of flannel plug-in.
# cd ~ && mkdir flannel && cd flannel
# curl -O https://raw.githubusercontent.com/coreos/flannel/master/Documentation/kube-flannel.yml
2)Startup
# kubectl apply -f ~/flannel/kube-flannel.yml
Log in to the karmada-host node and join the multi-cluster (the karmada.config below refers to the kubeconfig of the existing k8s cluster)
# hack/create-cluster.sh member1 $HOME/.kube/karmada.config
# go get github.com/karmada-io/karmada/cmd/karmadactl
# karmadactl join cluster01--cluster-kubeconfig=$HOME/.kube/karmada.config
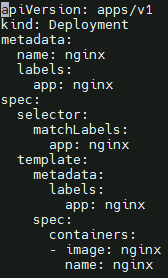
Nginx application deployment
- Create nginx deployment
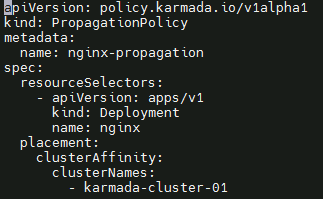
Create the nginx propagation policy
East-West Edge-to-Edge Networking
...
Environmental Information (CentOS8.0 4U8G)
Username & Password: root/Akraino2021
CPU Name | Role | IP | Workload |
|---|---|---|---|
Kubeedge-akraino-0001 | Cloud | 159.138.149.190 | K8S, docker, cloudcore |
Kubeedge-akraino-0002 | Edge Node | 119.8.35.111 | docker, edgecore, edgemesh |
Kubeedge-akraino-0003 | Edge Node | 182.160.10.130 | docker, edgecore, edgemesh |
Deployment Manual
Deploy cloud nodes (kubeEdge-cloud)
Disable boot firewall
# systemctl disable firewalld
Install Docker
# yum install wget container-selinux -y
# yum erase runc -y
# rpm -ivh containerd.io-1.2.6-3.3.el7.x86_64.rpm
Note: The above steps do not need to be operated in centos7
# update-alternatives --set iptables /usr/sbin/iptables-legacy
# yum install -y yum-utils device-mapper-persistent-data lvm2 && yum-config-manager --add-repo https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo && yum makecache
# yum -y install docker-ce
# systemctl enable docker.service && systemctl start docker
Configure yum source
[root@kubeEdge-cloud ~]# cat <<EOF > /etc/yum.repos.d/kubernetes.repo
[kubernetes]
name=Kubernetes
baseurl=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/repos/kubernetes-el7-x86_64
enabled=1
gpgcheck=1
repo_gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/yum-key.gpg https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/rpm-package-key.gpg
EOF
Install Kubeadm, kubectl
# yum makecache
# yum install kubelet-1.21.0-0.x86_64 kubeadm-1.21.0-0.x86_64 kubectl-1.21.0-0.x86_64
Note: The current KubeEdge version does not match the 1.22 version of K8s, and the latest version cannot be installed.
Configure the kernel parameters
[root@kubeEdge-cloud ~]# cat <<EOF > /etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1
vm.swappiness=0
EOF
[root@kubeEdge-cloud ~]# sysctl --system
[root@kubeEdge-cloud ~]# modprobe br_netfilter
[root@kubeEdge-cloud ~]# sysctl -p /etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf
Load ipvs related kernel modules
If you reboot, you need to reload (it can be written in /etc/rc.local to automatically load at boot)
[root@ke-cloud ~]# modprobe ip_vs
[root@ke-cloud ~]# modprobe ip_vs_rr
[root@ke-cloud ~]# modprobe ip_vs_wrr
[root@ke-cloud ~]# modprobe ip_vs_sh
[root@ke-cloud ~]# modprobe nf_conntrack_ipv4
Check whether loading is successful
[root@ke-cloud ~]# lsmod | grep ip_vs
Pull Mirror
[root@kubeEdge-cloud ~]# kubeadm config images list
[root@kubeEdge-cloud ~]# kubeadm config images pull
Initialize the cluster
[root@ke-cloud ~]# kubeadm init --kubernetes-version=v1.17.9 \
--pod-network-cidr=10.244.0.0/16 \
--apiserver-advertise-address=192.168.0.238 \
--ignore-preflight-errors=Swap
Deploy Cloudcore
Prerequisites: install golang
[root@kudeEdge-cloud ~]# git clone https://github.com/kubeedge/kubeedge $GOPATH/src/github.com/kubeedge/kubeedge
[root@kudeEdge-cloud ~]# cd $GOPATH/src/github.com/kubeedge/kubeedge
[root@kudeEdge-cloud ~]# make all WHAT=keadm
[root@kudeEdge-cloud ~]# keadm init --advertise-address="192.168.0.238"
Deploy edge nodes (edgemesh version is release1.7)
- Install docker same as before
- Obtain the token on the cloud node
[root@kudeEdge-cloud ~]# keadm gettoken
- Install edgecore and mqtt
[root@kudeEdge-cloud ~]# keadm join --cloudcore-ipport=192.168.1.66:10000 --token=“上一步骤获取的token”
--token="token obtained in the previous step"
- Modify the edgecore configuration
[root@kudeEdge-cloud ~]# vim /etc/kubeedge/config/edgecore.yaml
modules:
..
edgeMesh:
enable: false
metaManager:
metaServer:
enable: true
..
- Restart edgecore
[root@kudeEdge-cloud ~]# systemctl restart edgecore
- Modify cloudcore configuration and restart cloudcore
[root@kudeEdge-cloud ~]# vim /etc/kubeedge/config/cloudcore.yaml
modules:
..
dynamicController:
enable: true
..
- Pull EdgeMesh code and build EdgeMesh image
[root@kudeEdge-cloud ~]# docker build -t edgemesh:0.1 -f build/Dockerfile .
- Deploy EdgeMesh
Modify the following configuration file, modify service-cluster-ip-range.
[root@kudeEdge-cloud ~]# kubectl apply -f build/kubernetes/edgemesh/03-configmap.yaml
[root@kudeEdge-cloud ~]# kubectl apply -f build/kubernetes/edgemesh/04-daemonset.yaml
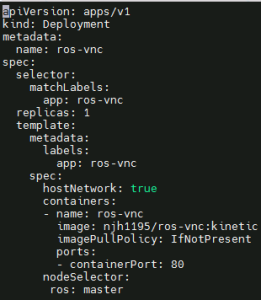
Deploy ROS application
Create ros-deployment-master.yaml and deploy
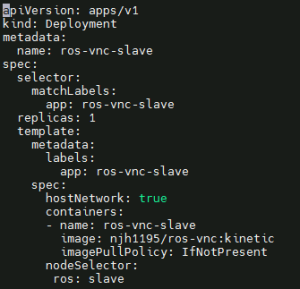
Create ros-deployment-slave.yaml and deploy
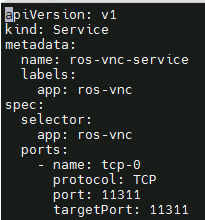
Create ros-master-service.yaml and deploy
ros application master node operation
Open the master node page, http://182.160.10.130:80
Refer to the operation of https://hub.docker.com/r/njh1195/ros-vnc:
- Open the terminal page and execute "roscore" to start roscore
- Open the second terminal page and execute "roslaunch turtlebot3_gazebo multi_turtlebot3.launch”
- multi_turtlebot3.launch" to start three simulation robots
- Open the third terminal page and execute "ROS_NAMESPACE=tb3_0 roslaunch
- turtlebot3_slam turtlebot3_gmapping.launch set_base_frame:=tb3_0/base_footprint set_odom_frame:=tb3_0/odom set_map_frame:=tb3_0/map”, set_map_frame:=tb3_0/map" to start the first robot scan on the master node.
Open the fourth terminal page and execute "roslaunch turtlebot3_gazebo
multi_map_merge.launch" to open the merge program.
Generate a point source map and execute "rosrun rviz rviz -d `rospack find
- turtlebot3_gazebo`/rviz/multi_turtlebot3_slam.rviz”
ros application master node operation
Open the slave node page, http://159.138.49.1:80
Refer to the operation of https://hub.docker.com/r/njh1195/ros-vnc:
- Open the terminal page and configure ros-master's access service. The file is in /root/.bashrc.
Add the following configuration at the end of the file to configure the master access address and slave address:
- Open the second terminal page and execute "ROS_NAMESPACE=tb3_1 roslaunch
- turtlebot3_slam turtlebot3_gmapping.launch
set_base_frame:=tb3_1/base_footprint set_odom_frame:=tb3_1/odom
set_map_frame:=tb3_1/map", open the graphic scan of another room.
- Check whether the point source graph is Merged in the master node.