- Blueprint overview/Introduction
- Platform Architecture
- Main Progresses for Release 4
- Hardware and Software Management
- Licensing
Blueprint overview/Introduction
Connected Vehicle Blueprint(CVB) is an Akraino approved blueprint and part of Akraino Edge Stack. The project is completely focused on Connected Vehicle Application run on Edge Computing.
Use Case
The use cases for the Connected Vehicle Blueprint are itemized below. For R4, we release the latest Microservice Platform Tars, which supports the multiple connected vehicle application deployment/management/orchestration/monitor.
UseCases | value proposition |
Smarter Navigation | Real-time traffic information update, reduces the latency from minutes to seconds, figure out the most efficient way for drivers. |
Safe Drive Improvement | Figure out the potential risks which can NOT be seen by the driver. |
Reduce traffic violation | Let the driver understand the traffic rule in some specific area. For instance, change the line prior to a narrow street, avoiding the opposite way drive in the one-way road, avoiding car pool lane when a single driver and so on. |
Cooperative vehicle and infrastructure system | Real time road objects status is obtained by roadside sensing system. Based on the sensing data, the vehicle obtains the traffic warning and driving assistance informationwhich threatens itself. |
Test case: The roadside camera recognizes the vehicles and pedestrians on the road through the edge computing server, and then pushes the pedestrian warning to the host vehicle (blue vehicle) .
Overall application Architecture
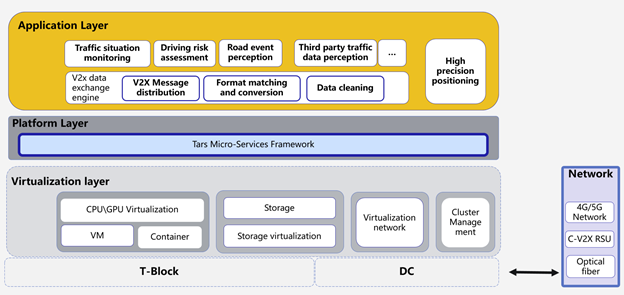
The following picture depicts the application architecture of the Connect Vehicle Blueprint, which consists of the following key components:
- Commodity Hardware, Arm/X86 Physical Server.
- Virtualization Layer.
- Tars Microservice Platform layer.
- Connected Vehicle Applications layer.
Connected Vehicle Applications include roadside traffic situation monitoring, driving risk assessment, road event perception, high percision positioning, and so on.
Overall deployment Architecture
The following picture depicts the architecture of the Connect Vehicle Blueprint, which consists of the following key components:
- Commodity Hardware, Arm/X86 Physical Server.
- IaaS Software, like Openstack, IaaS and so on
- Tars Microservice Platform
- Connected Vehicle Applications
The combination of Commodity Hardware and IaaS Software provides flexible deployments, like Bare Metal, Virtual Machine as well as Container.
Tars is a microservice framework that can manage/monitor/deploy the connected vehicle applications in the edge and data center. Tars can be flexibly deployed in Bare Metal, Virtual Machine as well as Container.
Connected Vehicle Applications are some different applications that fulfill Accurate Location, Smarter Navigation, Safe Drive Improvement, Reduce traffic violations, and cooperative vehicle infrastructure system.
.
Platform Architecture
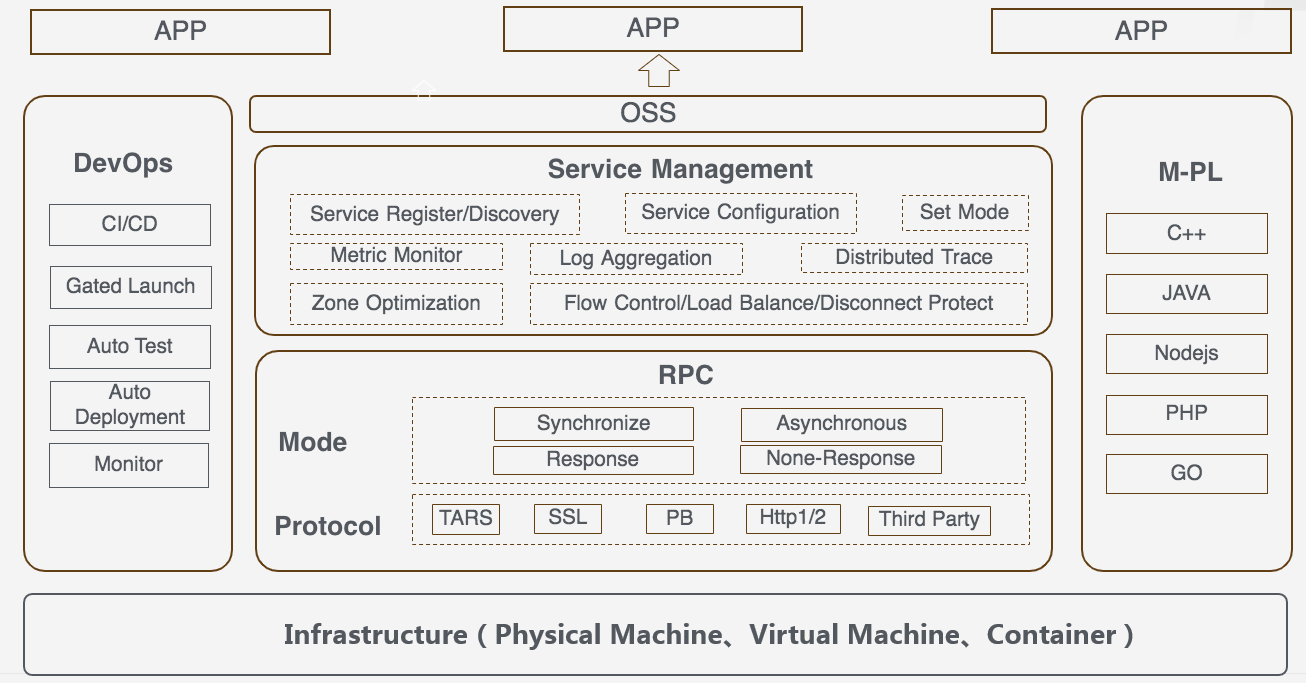
Software Platform Architecture
The following is the general architecture of Tars, which is a major component in R4.
Refer to the enclosed PDF document for the detail Tars introduction.
Main Progresses for Release 4
Release 4 is the 4th release for Connected Vehicle Blueprint.
Build Of Materials (BOM) / Hardware requirements
Connected Vehicle Blueprint can be flexibly deployed in Bare Metal, Virtual Machine as well as the container.
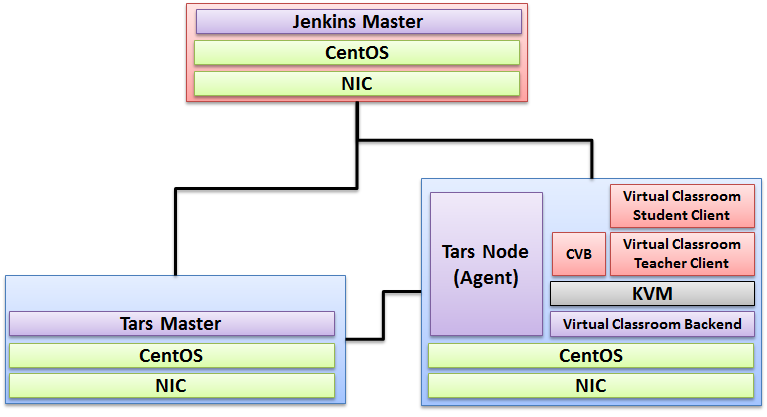
For R4, we deploy it in Intel Pod1 Akraino LAB for Release. The detailed hardware is itemized below:
Hostname | Core | RAM | HDD | NIC | Role |
Node-0 | 8 | 40GB | 3TB | 10GB | Jenkins Master |
Node-1 | 8 | 96GB | 3TB | 10GB | Tars Framework 2.4.13 |
Node-2 | 8 | 96GB | 3TB | 10GB | Tars Node (CVB + Type4 Application + Virtual Classroom Teacher Client + Virtual Classroom Student Client) |
Tars is an edge compute microservice platform with low latency, high quality.
Notes
Hardware and Software Management
Licensing
Components | Link | License | Akraino Release target |
| Tars | https://github.com/TarsCloud/Tars/releases/tag/v2.4.13 | BSD 3-Clause License | R4 |
| IEC | https://gerrit.akraino.org/r/#/admin/projects/iec - v3.0 | Apache License 2.0 | R4 |